 During the Copenhagen kerfuffle a lot of interesting stuff hit the web: here’s something that deserves a bit more air – a Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS) special issue on tipping elements in the earth system, edited by John Schellnhuber, the director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research in Germany.
During the Copenhagen kerfuffle a lot of interesting stuff hit the web: here’s something that deserves a bit more air – a Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS) special issue on tipping elements in the earth system, edited by John Schellnhuber, the director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research in Germany.
Tipping elements (or points, as Malcolm Gladwell would have them) are changes that once started take on a life of their own, and can’t easily be returned to their original state. In the climate system that might be the rapid loss of an ice sheet in a few decades or hundreds of years, while regrowing it might take many thousands. The PNAS special issue deals with nine: dust production in the Bodélé Depression in Chad, ENSO, Arctic sea ice and ice sheets, the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, deep ocean hydrates (not shallow sea bed, Siberian methane) — David Archer dubs them a “slow tipping point”, the Amazon rainforest (no “Amazongate” here, just a confirmation that concern is justified), monsoons, oceans, and policy responses to the climate challenge. And the best thing is that all the articles are available online, free (click on the link above). Schellnhuber contributes an introduction, and the Potsdam press release also provides a good overview. For some introductory thoughts, check out Tim Lenton’s discussion here.
Another recent example of a real tipping point is the Pine Island Glacier in West Antarctica. Recent modelling suggests that the glacier’s grounding line retreated beyond a ridge in 1996, and is now free to retreat by several hundred kilometres inland. This could happen in a hundred years and result in the loss of half of the ice in the glacier — enough to raise sea level by 24cm. New Scientist reports:
Observations already show that the model severely underestimates the rate at which PIG’s grounding line is retreating, says Katz. “Ours is a simple model of an ice sheet that neglects some important physics,” says Katz. “The take-home message is that we should be concerned about tipping points in West Antarctica and we should do a lot more work to investigate,” he says.
Amen to that.



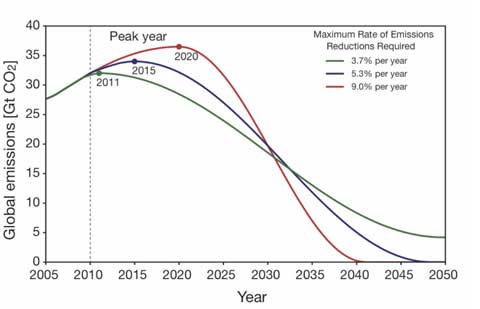
 The Copenhagen climate conference (
The Copenhagen climate conference (