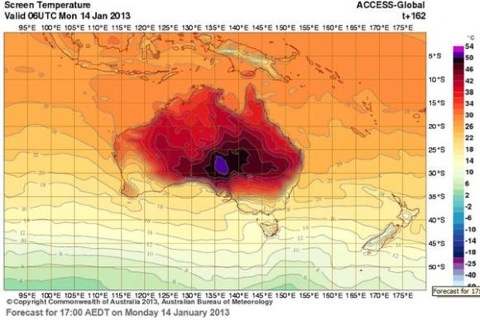
Australia is gripped by a massive heatwave, records are tumbling and fires are burning across the continent. I’m not going to attempt a comprehensive post on the subject — events are moving too fast — but I would like to note a few things. The Bureau of Meteorology forecast chart above (courtesy of Watching The Deniers) for next Monday has forced BOM to add new colours to the hot end of the range, to allow for forecast temperatures over 52ºC — well above the previous national record high of 50.7ºC. Meanwhile the current heatwave has already set a new record for the number of consecutive days where the national average temperature has exceeded 39ºC — now running at seven days, with the heat forecast to continue. That’s the average temperature for the whole of the continent, which is no small place. The previous record was four consecutive days, set in 1973.
The Sydney Morning Herald has a good summary of the records being broken here. See also: Jeff Masters, Climate Progress, New Scientist and the Guardian.
NASA’s Earth Observatory provides this overview of the fires in Tasmania over the weekend that caused chaos and destruction in the normally cool state — Hobart hit an all time high temperature of 41.8ºC, a full degree above its previous record.
Fire danger in parts of New South Wales has been classified as catastrophic, and this NASA Worldview image for Jan 8th appears to show smoke from fires in southern NSW streaming out to the east and over the sea towards New Zealand.
Ben Cubby at the SMH pulls together reactions from the scientific community under the headline “Get used to record breaking heat”, and one quote struck me rather forcefully:
“Those of us who spend our days trawling – and contributing to – the scientific literature on climate change are becoming increasingly gloomy about the future of human civilisation,’’ said Liz Hanna, convener of the human health division at the Australian National University’s Climate Change Adaptation Network.
As George Monbiot notes in the Guardian today, in a column excoriating Australian opposition leader Tony Abbott for his climate denial:
Australia’s new weather demands a new politics; a politics capable of responding to an existential threat.
My comment? That’s what the whole bloody world needs.



 What makes this event significant, is the role Arctic sea ice plays as a reflector of solar energy. Ice is white and therefore reflects a large part of incoming sunlight back out to space. But where there is no ice, dark ocean water absorbs most of the sunlight and thus heats up. The less ice there is, the more the water heats up, melting more ice. This
What makes this event significant, is the role Arctic sea ice plays as a reflector of solar energy. Ice is white and therefore reflects a large part of incoming sunlight back out to space. But where there is no ice, dark ocean water absorbs most of the sunlight and thus heats up. The less ice there is, the more the water heats up, melting more ice. This 
 James Hansen and two fellow-authors have circulated a new paper which they will be submitting for publication,
James Hansen and two fellow-authors have circulated a new paper which they will be submitting for publication,