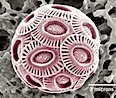
 Before you ask, the picture shows the shell of a coccolithophore, and it’s in trouble. We’ve been adding a lot of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, and a good chunk of it has ended up in the oceans. The water is getting more acidic, and some sea creatures are finding it harder to build their shells – which has the potential to disrupt the entire oceanic food web. We know it’s a problem, we know it’s happening, but we didn’t expect it be happening as fast as a recent research programme has found [Herald, Telegraph]. According to one of the scientists involved, “the coastal ocean acidification train has left the station, and there’s not much we can do to derail it.” Another excellent reason to cut carbon emissions, if one was needed.
Before you ask, the picture shows the shell of a coccolithophore, and it’s in trouble. We’ve been adding a lot of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, and a good chunk of it has ended up in the oceans. The water is getting more acidic, and some sea creatures are finding it harder to build their shells – which has the potential to disrupt the entire oceanic food web. We know it’s a problem, we know it’s happening, but we didn’t expect it be happening as fast as a recent research programme has found [Herald, Telegraph]. According to one of the scientists involved, “the coastal ocean acidification train has left the station, and there’s not much we can do to derail it.” Another excellent reason to cut carbon emissions, if one was needed.
More on methane: research on a rapid release of methane hydrates 635 million years ago hints that modern warming could trigger a similar cascade of gas release, with catastrophic results for the planet’s climate [Science Daily News, Wired]. Wired also has an excellent backgrounder on methane hydrates, discussing how they might be turned into a source of energy, while the BBC reports that the recent rise in methane in the atmosphere looks as though it is coming from thawing wetlands in the Arctic. In better news, NZ scientists have completed deciphering the genome of one of the methanogens that live in the rumens of cattle and sheep (Stuff, Yahoo/xtra). With luck and a lot of hard work, this might lead to methods of cutting methane emissions from livestock, and eventually play a key role in reducing agricultural emissions around the world.
Some light reading for the weekend: Yale’s environment360 is a new web site from the Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies, launched this month with some interesting and challenging articles from writers like Elizabeth Kolbert, Bill McKibben, and Fred Pearce amongst others. Worth checking out.
For those with more than a few minutes to spare, I can recommend The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity review [PDF] released this week. It’s an attempt to put a rational value on the services nature provides, to allow a Stern Review-type of cost benefit analysis of losing or retaining biodiversity [Herald, BBC, Guardian]. Climate change is only one contributor to biodiversity loss, but it could rapidly become the most important, and it’s the world’s poor that will suffer most.