 This editorial was published yesterday by 56 newspapers around the world in 20 languages including Chinese, Arabic and Russian. No newspapers in New Zealand or Australia carried the message. As a call to action, I believe it’s worth featuring here in full, and I am happy to endorse both the content and the sentiment expressed. The text was drafted by a Guardian team during more than a month of consultations with editors from more than 20 of the papers involved. Like the Guardian most of the newspapers took the unusual step of featuring the editorial on their front page.
This editorial was published yesterday by 56 newspapers around the world in 20 languages including Chinese, Arabic and Russian. No newspapers in New Zealand or Australia carried the message. As a call to action, I believe it’s worth featuring here in full, and I am happy to endorse both the content and the sentiment expressed. The text was drafted by a Guardian team during more than a month of consultations with editors from more than 20 of the papers involved. Like the Guardian most of the newspapers took the unusual step of featuring the editorial on their front page.
Today 56 newspapers in 45 countries take the unprecedented step of speaking with one voice through a common editorial. We do so because humanity faces a profound emergency.
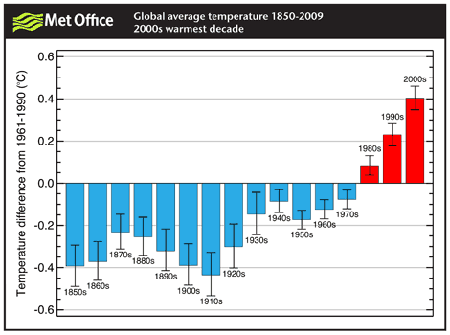
Unless we combine to take decisive action, climate change will ravage our planet, and with it our prosperity and security. The dangers have been becoming apparent for a generation. Now the facts have started to speak: 11 of the past 14 years have been the warmest on record, the Arctic ice-cap is melting and last year’s inflamed oil and food prices provide a foretaste of future havoc. In scientific journals the question is no longer whether humans are to blame, but how little time we have got left to limit the damage. Yet so far the world’s response has been feeble and half-hearted.
Climate change has been caused over centuries, has consequences that will endure for all time and our prospects of taming it will be determined in the next 14 days. We call on the representatives of the 192 countries gathered in Copenhagen not to hesitate, not to fall into dispute, not to blame each other but to seize opportunity from the greatest modern failure of politics. This should not be a fight between the rich world and the poor world, or between east and west. Climate change affects everyone, and must be solved by everyone.
The science is complex but the facts are clear. The world needs to take steps to limit temperature rises to 2ºC, an aim that will require global emissions to peak and begin falling within the next 5-10 years. A bigger rise of 3-4ºC — the smallest increase we can prudently expect to follow inaction — would parch continents, turning farmland into desert. Half of all species could become extinct, untold millions of people would be displaced, whole nations drowned by the sea. The controversy over emails by British researchers that suggest they tried to suppress inconvenient data has muddied the waters but failed to dent the mass of evidence on which these predictions are based.
Few believe that Copenhagen can any longer produce a fully polished treaty; real progress towards one could only begin with the arrival of President Obama in the White House and the reversal of years of US obstructionism. Even now the world finds itself at the mercy of American domestic politics, for the president cannot fully commit to the action required until the US Congress has done so.
But the politicians in Copenhagen can and must agree the essential elements of a fair and effective deal and, crucially, a firm timetable for turning it into a treaty. Next June’s UN climate meeting in Bonn should be their deadline. As one negotiator put it: “We can go into extra time but we can’t afford a replay.”
At the deal’s heart must be a settlement between the rich world and the developing world covering how the burden of fighting climate change will be divided — and how we will share a newly precious resource: the trillion or so tonnes of carbon that we can emit before the mercury rises to dangerous levels.
Rich nations like to point to the arithmetic truth that there can be no solution until developing giants such as China take more radical steps than they have so far. But the rich world is responsible for most of the accumulated carbon in the atmosphere – three-quarters of all carbon dioxide emitted since 1850. It must now take a lead, and every developed country must commit to deep cuts which will reduce their emissions within a decade to very substantially less than their 1990 level.
Developing countries can point out they did not cause the bulk of the problem, and also that the poorest regions of the world will be hardest hit. But they will increasingly contribute to warming, and must thus pledge meaningful and quantifiable action of their own. Though both fell short of what some had hoped for, the recent commitments to emissions targets by the world’s biggest polluters, the United States and China, were important steps in the right direction.
Social justice demands that the industrialised world digs deep into its pockets and pledges cash to help poorer countries adapt to climate change, and clean technologies to enable them to grow economically without growing their emissions. The architecture of a future treaty must also be pinned down – with rigorous multilateral monitoring, fair rewards for protecting forests, and the credible assessment of “exported emissions” so that the burden can eventually be more equitably shared between those who produce polluting products and those who consume them. And fairness requires that the burden placed on individual developed countries should take into account their ability to bear it; for instance newer EU members, often much poorer than “old Europe”, must not suffer more than their richer partners.
The transformation will be costly, but many times less than the bill for bailing out global finance — and far less costly than the consequences of doing nothing.
Many of us, particularly in the developed world, will have to change our lifestyles. The era of flights that cost less than the taxi ride to the airport is drawing to a close. We will have to shop, eat and travel more intelligently. We will have to pay more for our energy, and use less of it.
But the shift to a low-carbon society holds out the prospect of more opportunity than sacrifice. Already some countries have recognized that embracing the transformation can bring growth, jobs and better quality lives. The flow of capital tells its own story: last year for the first time more was invested in renewable forms of energy than producing electricity from fossil fuels.
Kicking our carbon habit within a few short decades will require a feat of engineering and innovation to match anything in our history. But whereas putting a man on the moon or splitting the atom were born of conflict and competition, the coming carbon race must be driven by a collaborative effort to achieve collective salvation.
Overcoming climate change will take a triumph of optimism over pessimism, of vision over short-sightedness, of what Abraham Lincoln called “the better angels of our nature”.
It is in that spirit that 56 newspapers from around the world have united behind this editorial. If we, with such different national and political perspectives, can agree on what must be done then surely our leaders can too.
The politicians in Copenhagen have the power to shape history’s judgment on this generation: one that saw a challenge and rose to it, or one so stupid that we saw calamity coming but did nothing to avert it. We implore them to make the right choice.
Links: Guardian original, how the editorial was compiled, the 56 newspapers. Distributed under a Creative Commons license.
Like this:
Like Loading...

 This editorial was published yesterday by 56 newspapers around the world in 20 languages including Chinese, Arabic and Russian. No newspapers in New Zealand or Australia carried the message. As a call to action, I believe it’s worth featuring here in full, and I am happy to endorse both the content and the sentiment expressed. The text was drafted by a Guardian team during more than a month of consultations with editors from more than 20 of the papers involved. Like the Guardian most of the newspapers took the unusual step of featuring the editorial on their front page.
This editorial was published yesterday by 56 newspapers around the world in 20 languages including Chinese, Arabic and Russian. No newspapers in New Zealand or Australia carried the message. As a call to action, I believe it’s worth featuring here in full, and I am happy to endorse both the content and the sentiment expressed. The text was drafted by a Guardian team during more than a month of consultations with editors from more than 20 of the papers involved. Like the Guardian most of the newspapers took the unusual step of featuring the editorial on their front page.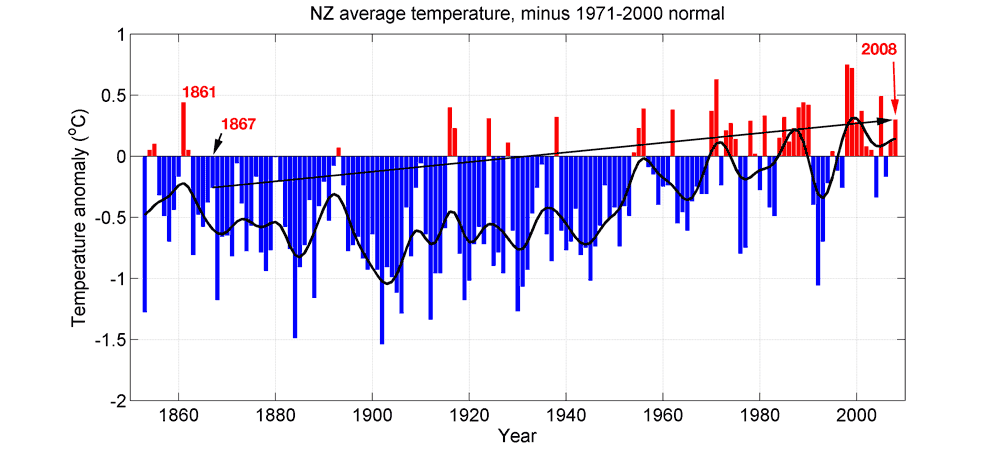 NIWA has
NIWA has 