 It is profoundly depressing to hear pundits and politicians talking about the prospects for economic growth with no reference to either equity or environmental constraints. In the case of New Zealand a “rock star” economy can apparently develop accompanied by dismaying levels of child poverty, excited expectations of new oil and gas discoveries which spell disaster for the climate, and a burgeoning dairy industry paying scant attention to the environmental consequences of its rapid growth.
It is profoundly depressing to hear pundits and politicians talking about the prospects for economic growth with no reference to either equity or environmental constraints. In the case of New Zealand a “rock star” economy can apparently develop accompanied by dismaying levels of child poverty, excited expectations of new oil and gas discoveries which spell disaster for the climate, and a burgeoning dairy industry paying scant attention to the environmental consequences of its rapid growth.
Fortunately there are more discerning economists on the world stage for whom economic growth is only welcome when it means an end to poverty and when it fully respects strict environmental limits. Jeffrey Sachs, Director of the Earth Institute at Columbia University, is an outstanding example. His latest book The Age of Sustainable Development is heavily focused on the ending of poverty in parts of the world where it remains endemic and is relentless in its recognition of the severe environmental strains that economic development and soaring population growth are placing on the earth systems on which human life depends.
The book was developed as part of a global open online course of the same name offered by the Earth Institute and already taken, Sachs reports, by tens of thousands of students around the world.

 In my post at The Daily Blog today —
In my post at The Daily Blog today —  Welcome to the fiftheenth post in the Sustainable Energy without the Hot Air – A New Zealand Perspective series. After our previous posts on
Welcome to the fiftheenth post in the Sustainable Energy without the Hot Air – A New Zealand Perspective series. After our previous posts on 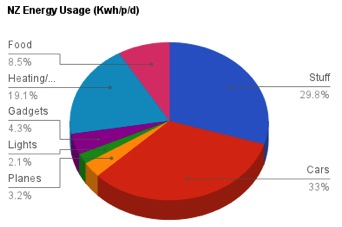
 Welcome to the fourteenth post in the Sustainable Energy without the Hot Air – A New Zealand Perspective series. After our previous posts on
Welcome to the fourteenth post in the Sustainable Energy without the Hot Air – A New Zealand Perspective series. After our previous posts on
You must be logged in to post a comment.