A stunning image of a massive bloom of phytoplankton off the Chatham Islands (to the east of NZ — that’s Wellington and the Wairarapa in the top left corner), snapped by NASA’s Aqua satellite on December 5th and featured this week at NASA’s excellent Earth Observatory. Click on the image to see the full (4MB) image with lots more detail. NASA describes the region as a carbon sink, because the mixing of cold but nutrient rich deep water from Antarctica, with warm nutrient-poor (but iron-rich) sub tropical water provides the perfect recipe for large phytoplankton blooms — especially in spring and autumn. A major constituent of these blooms is usually huge numbers of coccolithophores, an important component in the oceanic carbon cycle, as I pointed out the last time the Chathams featured on the Earth Observatory.
Tag: coccolithophore
You don’t know what you’ve got ’til it’s gone
 Biodiversity continues its steady decline. A team of scientists have this week published a study in Science confirming that fact. Governments in 2002 at a summit on the Convention on Biological Diversity agreed to aim to halt biodiversity loss by the year 2010. When experts meet in Nairobi on May 10 it will be to face the news that they have failed. For example, since 1970 the world’s animal population has decreased by 30%, mangroves and sea grasses have shrunk in area by 20%, and live-coral coverage has fallen by 40%. “The state of biodiversity is definitely showing a rapid decline,” says Matt Foster, one of the lead authors on the Sciencepaper. “And the pressure just keeps increasing.”
Biodiversity continues its steady decline. A team of scientists have this week published a study in Science confirming that fact. Governments in 2002 at a summit on the Convention on Biological Diversity agreed to aim to halt biodiversity loss by the year 2010. When experts meet in Nairobi on May 10 it will be to face the news that they have failed. For example, since 1970 the world’s animal population has decreased by 30%, mangroves and sea grasses have shrunk in area by 20%, and live-coral coverage has fallen by 40%. “The state of biodiversity is definitely showing a rapid decline,” says Matt Foster, one of the lead authors on the Sciencepaper. “And the pressure just keeps increasing.”
It’s not that governments have made no efforts. The amount of protected land has steadily increased around the world, as has the area of sustainably managed forests. Increased money is being spent on biodiversity aid. But we’re still shouldering other species out of our way. And in doing so we’re attacking our own well-being. “We all benefit from biodiversity and we all hurt when it’s lost,” says Foster.
Climate change is only one of the ways in which humankind is contributing to biodiversity loss. But it’s worth reminding ourselves that it is seriously exacerbating the process. I’ve been re-reading a fine book by Michael Novacek, Terra, published in 2007. He’s a distinguished paleontologist, Provost of Science at the American Museum of Natural History. He was involved in the splendid Darwin exhibition put together by the Museum of Natural History which I was fortunate to be able to see when it was brought to the Auckland Museum in 2007. That’s when I bought his book. It’s subtitled Our 100-Million-Year-Old Ecosystem –- and the Threats That Now Put It at Risk. I think some points from his chapter on how the current warming is contributing to biodiversity loss are worth recounting here.
He notes changes in the activity of 694 species whose life history data between 1951 and 2001 has been studied. A 2003 review found on average the species were either breeding, blooming, or doing other seasonally related activities 5.3 days earlier each decade.
The warming trend has also set species in motion. Some move poleward. Other species have moved upslope. Some have simply contracted and their surviving, marginalised populations have been reduced to precariously low levels.
Novacek is interesting on the evolutionary processes at work in the organisms affected by rapid alteration of range. The hardy colonisers which often establish at the leading edge of the shift may have a very low level of gene diversity, leaving them susceptible to further environmental changes. The populations at the trailing edge of the migration may have more genetic diversity, but they will start to fragment as the environmental conditions break up their preferred habitats. The rate of environmental challenge may determine how a population’s genetic makeup and evolution are transformed. Slow change may be easier for the species to maintain genetic diversity at levels that allow it to persist. Drastic and rapid change make it more vulnerable. Simply moving to a cooler habitat does not guarantee that the genetic composition of the migrating populations will be robust enough to sustain them.
It’s made more complex by the bewildering diversity of examples in nature. Some species, especially in tropical and mountainous regions, may be buffered by the amount of genetic variation already resident in their populations. Other genetic studies suggest that climate change has easily outrun the rate at which a given population can adjust.
Novacek sees contemporary evidence that climate change in combination with other factors is killing off certain species. It seems to be the coup de grace for some coral species. Increasing ocean acidification also plays a part in the demise of coral and threatens the most abundant and ecologically important sea organisms, the coccolithophorids, foraminifera and pteropods which are vitally important food for many fish.
On land, organisms that live in lakes, streams, rivers, and other bodies of freshwater are highly endangered and are especially susceptible to climate change because they cannot escape its effects, being captive in their habitat.
Most threatened are the habitats and species at high latitudes, the northern tundra and polar deserts such as those on the Arctic islands and Antarctica as well as species inhabiting high Alpine or montane habitats at middle to low latitudes.
I liked the last sentence of his chapter. In the preceding sentences he noted what he regarded as encouraging signs of acceptance of the science of global warming. He recorded, however, still encountering individuals normally open to the discoveries of science who find it beyond belief that humans could disrupt the balance of the planet in such an enormous way. The final sentence: “But science has eventually convinced us before of the unbelievable.”
Beautiful haze
I’m a sucker for pictures from space, and this morning’s offering from NASA’s Earth Observatory site is a stunning view of the Chatham Islands, snapped by NASA’s Aqua satellite last Saturday (click on the picture to see the full size image). The turquoise clouds in the sea around the islands are a bloom of coccolithophores, a kind of phytoplankton that plays a significant role in the climate system. They have tiny skeletons made of carbonate, and sequester carbon as they die and their skeletons fall to the ocean floor, but they also affect planetary albedo (by making oceans more reflective), and give off dimethyl sulfide, an important source of particles to seed cloud formation. More here, and here.
I’d be very surprised if this picture doesn’t show up in the newspapers tomorrow, because a) it’s beautiful, and b) NASA doesn’t charge for the use of its images.
Friday on my mind (once more)
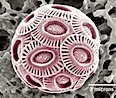 Before you ask, the picture shows the shell of a coccolithophore, and it’s in trouble. We’ve been adding a lot of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, and a good chunk of it has ended up in the oceans. The water is getting more acidic, and some sea creatures are finding it harder to build their shells – which has the potential to disrupt the entire oceanic food web. We know it’s a problem, we know it’s happening, but we didn’t expect it be happening as fast as a recent research programme has found [Herald, Telegraph]. According to one of the scientists involved, “the coastal ocean acidification train has left the station, and there’s not much we can do to derail it.” Another excellent reason to cut carbon emissions, if one was needed.
Before you ask, the picture shows the shell of a coccolithophore, and it’s in trouble. We’ve been adding a lot of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, and a good chunk of it has ended up in the oceans. The water is getting more acidic, and some sea creatures are finding it harder to build their shells – which has the potential to disrupt the entire oceanic food web. We know it’s a problem, we know it’s happening, but we didn’t expect it be happening as fast as a recent research programme has found [Herald, Telegraph]. According to one of the scientists involved, “the coastal ocean acidification train has left the station, and there’s not much we can do to derail it.” Another excellent reason to cut carbon emissions, if one was needed.
More on methane: research on a rapid release of methane hydrates 635 million years ago hints that modern warming could trigger a similar cascade of gas release, with catastrophic results for the planet’s climate [Science Daily News, Wired]. Wired also has an excellent backgrounder on methane hydrates, discussing how they might be turned into a source of energy, while the BBC reports that the recent rise in methane in the atmosphere looks as though it is coming from thawing wetlands in the Arctic. In better news, NZ scientists have completed deciphering the genome of one of the methanogens that live in the rumens of cattle and sheep (Stuff, Yahoo/xtra). With luck and a lot of hard work, this might lead to methods of cutting methane emissions from livestock, and eventually play a key role in reducing agricultural emissions around the world.
Some light reading for the weekend: Yale’s environment360 is a new web site from the Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies, launched this month with some interesting and challenging articles from writers like Elizabeth Kolbert, Bill McKibben, and Fred Pearce amongst others. Worth checking out.
For those with more than a few minutes to spare, I can recommend The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity review [PDF] released this week. It’s an attempt to put a rational value on the services nature provides, to allow a Stern Review-type of cost benefit analysis of losing or retaining biodiversity [Herald, BBC, Guardian]. Climate change is only one contributor to biodiversity loss, but it could rapidly become the most important, and it’s the world’s poor that will suffer most.


