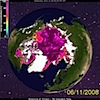
 The Arctic summer sea ice cover could be reduced by 2013 to “a few outcrops on islands near Greenland and Canada between mid-July and mid-September”, according to new research reported in The Observer [UK] today. The paper also suggests that this year could still see a new record minimum. Wieslaw Maslowski, the US Navy researcher who suggested in 2007 that the Arctic could be ice free by 2013, told Observer science editor Robin McKie:
The Arctic summer sea ice cover could be reduced by 2013 to “a few outcrops on islands near Greenland and Canada between mid-July and mid-September”, according to new research reported in The Observer [UK] today. The paper also suggests that this year could still see a new record minimum. Wieslaw Maslowski, the US Navy researcher who suggested in 2007 that the Arctic could be ice free by 2013, told Observer science editor Robin McKie:
‘It does not really matter whether 2007 or 2008 is the worst year on record for Arctic ice,’ Maslowski said. ‘The crucial point is that ice is clearly not building up enough over winter to restore cover and that when you combine current estimates of ice thickness with the extent of the ice cap, you get a very clear indication that the Arctic is going to be ice-free in summer in five years. And when that happens, there will be consequences.’
This is the first story I’ve found in a mainstream newspaper that has picked up on what those “consequences” might be, albeit in only the most general terms:
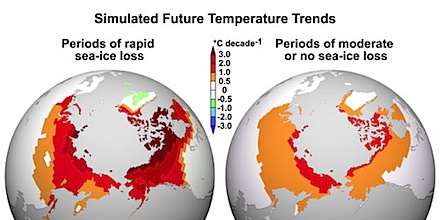
This startling loss of Arctic sea ice has major meteorological, environmental and ecological implications. The region acts like a giant refrigerator that has a strong effect on the northern hemisphere’s meteorology. Without its cooling influence, weather patterns will be badly disrupted, including storms set to sweep over Britain.
Or a run of warm wet summers.
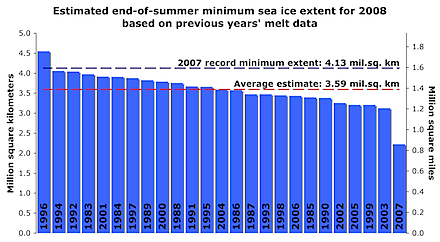
The paper also talked to Mark Serreze from the NSIDC about the speed up in melt over the last week:
‘[…]Beaufort Sea storms triggered steep ice losses and it now looks as if it will be a very close call indeed whether 2007 or 2008 is the worst year on record for ice cover over the Arctic. We will only find out when the cover reaches its minimum in mid-September.’
The fat lady may just have got back into the limo and returned to her hotel for a snack.
[Update 12/8: The NSIDC has updated (11/8) its Arctic news page, commenting on the effect of storms on the ice, and noting that Amundsen’s long version of the NW Passage will be open soon.]