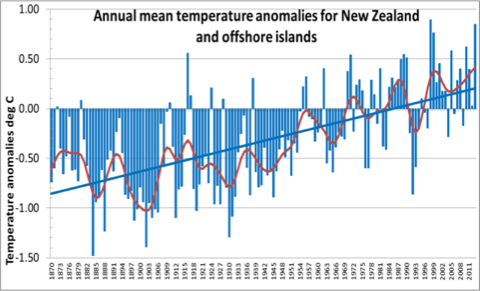
 NZ temperature expert Jim Salinger has been crunching last year’s data, and this morning confirmed that 2013 was a hot year in the New Zealand region — the second warmest in the long term record, beaten only by 1998. Based on 22 land stations and the three offshore islands, the annual average temperature was 0.84ºC above the 1961–1990 long term average of 12.17°C (1998 was +0.89ºC).
NZ temperature expert Jim Salinger has been crunching last year’s data, and this morning confirmed that 2013 was a hot year in the New Zealand region — the second warmest in the long term record, beaten only by 1998. Based on 22 land stations and the three offshore islands, the annual average temperature was 0.84ºC above the 1961–1990 long term average of 12.17°C (1998 was +0.89ºC).
Winter 2013 was the warmest ever recorded, and Masterton, Omarama, Timaru, Invercargill and the Chatham Islands set new annual temperature records. In the last ten years only two years (2004 and 2009) have been cooler than average, and the ten year mean temperature was 0.26ºC above average, the highest on record.
Source: Jim Salinger
During 2013 the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) was in a neutral phase, and the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation (IPO) was negative. According to Salinger, this favours more easterlies and north easterlies when temperatures are above average. Sea surface temperatures were also well above average, especially around the South Island and to the east of the country. Jim is also expecting 2014 to be warm:
ENSO neutral conditions are expected to persist at least until winter 2014, and negative IPO conditions are very likely to persist for the remainder of 2014. These conditions are expected to bring temperatures of +0.2 to +0.6°C above average for the New Zealand region.
Across the Tasman, Australia has just recorded its warmest year since records began — with a remarkable number of heat records being set. Final figures for the annual global average temperature on main terrestrial datasets has yet to be released, but the World Meteorological Organisation expects 2013 to be 6th warmest. A few days ago the University of Alabama in Huntsville revealed that its satellite temperature dataset provisionally put 2013 in 4th place since 1979.




You must be logged in to post a comment.