 Another day, another bet on sea ice. A few days ago, a regular reader of HT emailed to ask me if I could provide some support in a long series of comments to a post at Poneke! about the showing of Swindle. So I did (my contributions start here). And now I have another bet on this northern hemisphere summer’s sea ice minimum, with a commenter calling himself “malcolm” taking the Stoat position (cold side = more ice than last year, not something out of the Kama Sutra). So here’s an update on events up North. Consider it a form guide, if you will.
Another day, another bet on sea ice. A few days ago, a regular reader of HT emailed to ask me if I could provide some support in a long series of comments to a post at Poneke! about the showing of Swindle. So I did (my contributions start here). And now I have another bet on this northern hemisphere summer’s sea ice minimum, with a commenter calling himself “malcolm” taking the Stoat position (cold side = more ice than last year, not something out of the Kama Sutra). So here’s an update on events up North. Consider it a form guide, if you will.
Category: Climate science
Friday on my mind (once more)
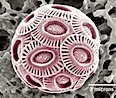 Before you ask, the picture shows the shell of a coccolithophore, and it’s in trouble. We’ve been adding a lot of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, and a good chunk of it has ended up in the oceans. The water is getting more acidic, and some sea creatures are finding it harder to build their shells – which has the potential to disrupt the entire oceanic food web. We know it’s a problem, we know it’s happening, but we didn’t expect it be happening as fast as a recent research programme has found [Herald, Telegraph]. According to one of the scientists involved, “the coastal ocean acidification train has left the station, and there’s not much we can do to derail it.” Another excellent reason to cut carbon emissions, if one was needed.
Before you ask, the picture shows the shell of a coccolithophore, and it’s in trouble. We’ve been adding a lot of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, and a good chunk of it has ended up in the oceans. The water is getting more acidic, and some sea creatures are finding it harder to build their shells – which has the potential to disrupt the entire oceanic food web. We know it’s a problem, we know it’s happening, but we didn’t expect it be happening as fast as a recent research programme has found [Herald, Telegraph]. According to one of the scientists involved, “the coastal ocean acidification train has left the station, and there’s not much we can do to derail it.” Another excellent reason to cut carbon emissions, if one was needed.
More on methane: research on a rapid release of methane hydrates 635 million years ago hints that modern warming could trigger a similar cascade of gas release, with catastrophic results for the planet’s climate [Science Daily News, Wired]. Wired also has an excellent backgrounder on methane hydrates, discussing how they might be turned into a source of energy, while the BBC reports that the recent rise in methane in the atmosphere looks as though it is coming from thawing wetlands in the Arctic. In better news, NZ scientists have completed deciphering the genome of one of the methanogens that live in the rumens of cattle and sheep (Stuff, Yahoo/xtra). With luck and a lot of hard work, this might lead to methods of cutting methane emissions from livestock, and eventually play a key role in reducing agricultural emissions around the world.
Some light reading for the weekend: Yale’s environment360 is a new web site from the Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies, launched this month with some interesting and challenging articles from writers like Elizabeth Kolbert, Bill McKibben, and Fred Pearce amongst others. Worth checking out.
For those with more than a few minutes to spare, I can recommend The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity review [PDF] released this week. It’s an attempt to put a rational value on the services nature provides, to allow a Stern Review-type of cost benefit analysis of losing or retaining biodiversity [Herald, BBC, Guardian]. Climate change is only one contributor to biodiversity loss, but it could rapidly become the most important, and it’s the world’s poor that will suffer most.
Look out, here comes tomorrow
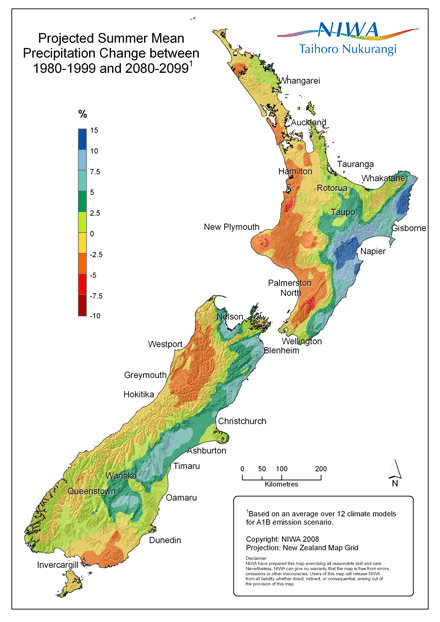 Hot off the presses: NIWA’s latest projections for the climate of New Zealand over the coming century were released this morning as part of a new MfE guidance manual (here, PDF) for local government. Based on IPCC modelling for AR3 and AR4 downscaled to local climate, plus early work with NIWA’s new regional climate model, the picture is broadly similar to earlier results: modest warming everywhere, a reduction in frosts and more hot days, increased frequency of droughts and heavy rainfall events, and steady sea level rise. NIWA’s press release is available at Scoop (link to full .doc here). At the same time the Ministry of Agriculture has released its latest EcoClimate report, which takes the new projections and assesses their impact on key agricultural sectors. I’ll be picking through these reports, and the associated coastal hazards guidance over the next few days, but here are a few of the headlines:
Hot off the presses: NIWA’s latest projections for the climate of New Zealand over the coming century were released this morning as part of a new MfE guidance manual (here, PDF) for local government. Based on IPCC modelling for AR3 and AR4 downscaled to local climate, plus early work with NIWA’s new regional climate model, the picture is broadly similar to earlier results: modest warming everywhere, a reduction in frosts and more hot days, increased frequency of droughts and heavy rainfall events, and steady sea level rise. NIWA’s press release is available at Scoop (link to full .doc here). At the same time the Ministry of Agriculture has released its latest EcoClimate report, which takes the new projections and assesses their impact on key agricultural sectors. I’ll be picking through these reports, and the associated coastal hazards guidance over the next few days, but here are a few of the headlines:
Swell maps, and other stories
 Time for another round up of climate-related news. Hot on the web today (for cartophiles, at least) is that Google Earth has gained a swag of new climate change related information, the result of collaboration between Google, the UK Government, the Met Office Hadley Centre and the British Antarctic Survey. The Climate Change in Our World project, launched at the Google Zeitgeist conference by UK PM Gordon Brown offers two new layers based on Hadley Centre predictions, BAS research in Antarctica, and impacts worldwide. You can animate global temperature changes, visit crumbling ice shelves, and view climate change impacts around the world. Google Earth blog here, download .kmz files here. Hours of geographical fun are guaranteed.
Time for another round up of climate-related news. Hot on the web today (for cartophiles, at least) is that Google Earth has gained a swag of new climate change related information, the result of collaboration between Google, the UK Government, the Met Office Hadley Centre and the British Antarctic Survey. The Climate Change in Our World project, launched at the Google Zeitgeist conference by UK PM Gordon Brown offers two new layers based on Hadley Centre predictions, BAS research in Antarctica, and impacts worldwide. You can animate global temperature changes, visit crumbling ice shelves, and view climate change impacts around the world. Google Earth blog here, download .kmz files here. Hours of geographical fun are guaranteed.
- A major new study finds strong links between recent climate change and large scale changes in the planet’s natural systems. It’s our fault, in other words [Nature (behind a paywall), BBC, Science Daily News, Guardian]. Lead author Cynthia Rosenzweig from the Goddard Institute for Space Studies in New York told the BBC “…look at all the effects this relatively low amount of warming has had. It reveals the sensitivity to relatively low amounts of warming in many physical and biological systems.” A key point for anyone who thinks that “only a few degrees” won’t make much difference.
- The growing number of humans on the planet is having a dramatic impact on wildlife populations, according to the Living Planet Index compiled by WWF and the Zoological Society of London. Populations of land-based species have fallen by 25%, marine by 28% and freshwater by 29% since 1970. We’re losing about 1% of all other species every year, and one of the “great extinction episodes” in the Earth’s history is under way, the index finds. [BBC, Independent, Guardian, Telegraph].
- More bad wildlife news: the 2008 Bird Red List “warns that long-term droughts and extreme weather puts additional stress on key habitats,” according to the BBC. “The assessment lists 1,226 species as threatened with extinction – one-in-eight of all bird species.“
- RNZ National’s science programme Our Changing World is always worth a listen, but last week’s (15/5/08) was a cracker. Ice core expert Richard Alley on Antarctica’s future, an update on the University of Waikato’s UltraCommuter EV, and one of the most cogent overviews of biofuel options I’ve ever heard from Doug Cameron, Chief Scientific Officer of Khosla Ventures, the Californian clean tech company. If those streaming links expire, podcast versions are available here, and the programme’s archive is here.
- Wired reports on Renault’s plans to make EVs for Israel, and then the world, and EcoGeek discovers that Audi intends to have EVs in production in ten years. They might have to hurry… (my son announced yesterday that “one day’ he intends to own a Porsche. I’m willing to bet that by the time he can afford one (if ever) it’ll be a hybrid or EV).
- #35 with a bullet! Tim Selwyn’s latest NZ blogosphere survey (at Tumeke!) finds that Hot Topic has moved up from #68 in February to #35 in March/April. I’d like to thank The Listener for making it all possible… 😉
What’s going on?
 The Heartland Institute’s inclusion of five New Zealand scientists in a list of “500 Scientists with Documented Doubts of Man-Made Global Warming Scares” (title has since changed to “500 Scientists Whose Research Contradicts Man-Made Global Warming Scares” – PDF here) is even more bogus than I originally thought.
The Heartland Institute’s inclusion of five New Zealand scientists in a list of “500 Scientists with Documented Doubts of Man-Made Global Warming Scares” (title has since changed to “500 Scientists Whose Research Contradicts Man-Made Global Warming Scares” – PDF here) is even more bogus than I originally thought.
The list is the product of the fertile imaginations of Dennis Avery and Fred Singer, and is “derived primarily from the citations” in their recent book Unstoppable Global Warming—Every 1,500 Years. They say in the introduction:
The following list includes more than 500 qualified researchers, their home institutions, and the peer-reviewed studies they have published in professional journals providing historic and/or physical proxy evidence that:
1) Most of the recent global warming has been caused by a long, moderate, natural cycle rather than by the burning of fossil fuels… [There are six more items, but you can read them for yourself]
So how did Jim get in there? He sent me a copy of the offending paper – Southwest Pacific temperatures: trends in maximum and minimum temperatures, Atmospheric Research 37 (1995) (copy here). It’s interesting enough, but not exactly earth-shattering. As the title suggests, it uses a then new data set for SW Pacific temperatures and looks for changes in maximum and minimum daily temperatures in the region. The paper states “Increases in concentrations of greenhouse gases and changes in cloudiness could be plausible mechanisms for the overall increase in both daily maximum and minimum temperatures.”
Avery and Singer list the paper in their first section, “studies finding evidence of the climate cycle”. Now I’ve read the paper in some detail, and I can’t find any reference to a 1,500 year cycle, or indeed a cycle of any kind. Perhaps Avery & Singer included it because Jim rides a bicycle?
In other words, the use of Salinger’s paper to support Avery & Singer’s hypothesis is entirely bogus. It’s scientific fraud, unethical, and just another example of how Heartland are prepared to encourage people to distort the truth in support of their political objectives. I hope Heartland’s apologists in New Zealand, the NZ Climate “Science” Coalition will share my outrage, and demand that Bast and co remove Salinger from the list immediately.
But I’m not holding my breath.
