 In his interview on TV3’s The Nation last weekend David Shearer declared a Labour Party policy on oil and gas drilling which, like the Government’s, fails to confront the reality of climate change. Drilling will continue. The approval processes will be improved, the regulations will be tight, the money gained will be used well, but drilling will continue. He acknowledged that “at the end of the day” fossil fuels are out. They cannot continue to be our future. But we can use them to transition to renewables. They can remain a strand in our development. ”There’s a potential there and while there’s a potential we should be looking at it.”
In his interview on TV3’s The Nation last weekend David Shearer declared a Labour Party policy on oil and gas drilling which, like the Government’s, fails to confront the reality of climate change. Drilling will continue. The approval processes will be improved, the regulations will be tight, the money gained will be used well, but drilling will continue. He acknowledged that “at the end of the day” fossil fuels are out. They cannot continue to be our future. But we can use them to transition to renewables. They can remain a strand in our development. ”There’s a potential there and while there’s a potential we should be looking at it.”
Transition is a word which acquires a convenient elasticity in the language of those who argue for the continued exploration for fossil fuels. We all realise that the change from fossil energy can’t happen overnight. There has to be a period of transition. But to use that fact to justify continued new exploration and development of fossil fuels is to rob the transition of all urgency and treat it rather as something we will need to gradually prepare for as fossil reserves are finally exhausted.
The message from the science is clear. If we burn more than a third of the fossil fuel reserves already discovered we will cause a level of warming likely to prove catastrophic for human society. Continue reading “Labour’s dodgy drilling policy avoids climate reality”

 At The Daily Blog today
At The Daily Blog today  Science journalist
Science journalist 

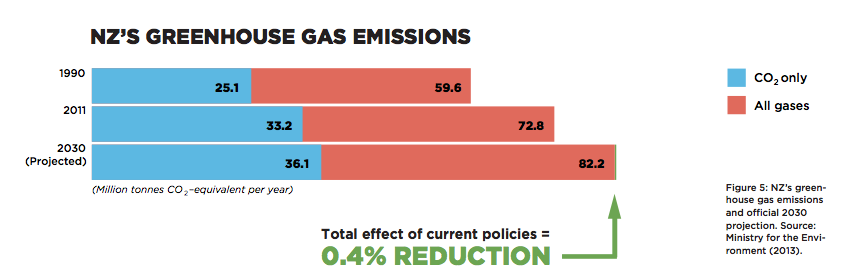
 Late last week, New Zealand’s far right ACT party was pleased
Late last week, New Zealand’s far right ACT party was pleased
You must be logged in to post a comment.